LRWC TREATMENT PROGRAMS
ICE/ Cocaine
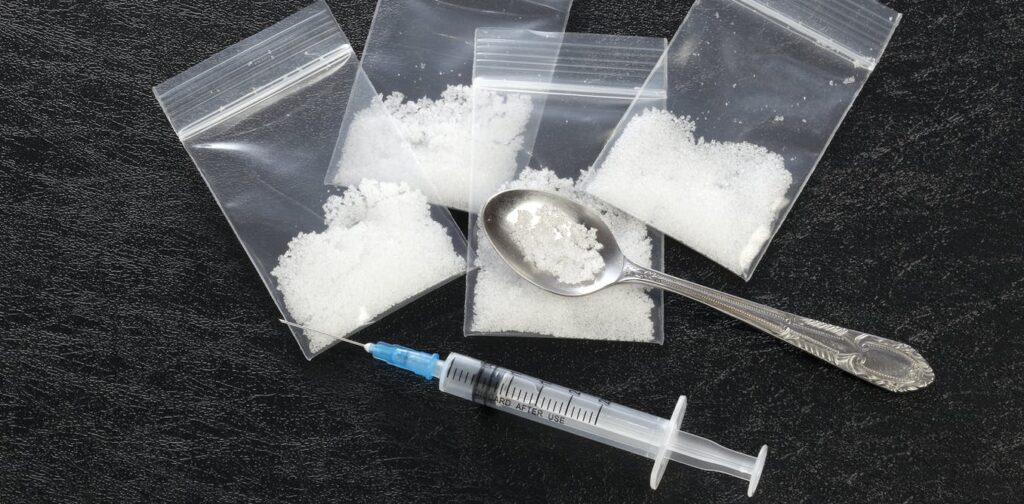
What is ICE?
Crystal methamphetamine (‘ice’, ice drug) is a stimulant drug, which means it speeds up the messages travelling between the brain and the body. It’s stronger, more addictive and therefore has more harmful side effects than the powder form of methamphetamine known as speed.
Ice usually comes as small chunky clear crystals that look like ice. It can also come as white or brownish crystal-like powder with a strong smell and bitter taste.
Other names
Crystal meth, shabu, crystal, glass, shard, P.
How is it used?
Ice is generally smoked (feel the effect almost immediately) or injected (15 to 30 seconds to feel the effects). It is sometimes swallowed (15 to 20 minutes to feel the effects) or snorted (3 to 5 minutes to feel the effects).
Other types of stimulants
1. Amphetamines
2.Betel nut
3.Caffeine
4.Cocaine
5.Khat
6.Mephedrone
7.Nicotine
8.Synthetic cathinones
Effects of ice
There is no safe level of drug use. Use of any drug always carries some risk. It’s important to be careful when taking any type of drug.
The effects of ice can last for up to 12 hours,2 but it might be hard to sleep for a few days after using the drug.
Ice affects everyone differently, but effects may include:
- 1. feelings of pleasure and confidence
- 2. increased alertness and energy
3. repeating simple things like itching and scratching
4. enlarged pupils and dry mouth
5. teeth grinding and excessive sweating
6. fast heart rate and breathing
7. reduced appetite
8. increased sex drive
If injecting drugs there is an increased risk of:
1. tetanus
2. infection
3. vein damage
If sharing needles there is an increased risk of:
1. Hepatitis B
2. Hepatitis C
3. HIV and AIDS
Snorting ice can damage the nasal passage and cause nose bleeds.
Overdose
If you take a large amount or have a strong batch, you could
overdose. Call an ambulance straight away by dialling triple zero (000) if you
have any of these symptoms (ambulance officers don’t need to involve the
police):
1. racing heartbeat and chest pain
2. breathing problems
3. fits or uncontrolled jerking
4. extreme agitation, confusion, clumsiness
5. sudden, severe headache
6. unconsciousness
7. stroke, heart attack or death